SEO Audit 101: Your Guide to a Foundational SEO Audit

With 93% of online experiences beginning with a search engine, there’s no arguing in the value of search
engine optimization. But how do you go about ranking well on search engines? The best place to start is to run a foundational SEO audit to understand how your website is doing, and what are the main areas to improve. With the help of several other SEOs, I’ve compiled a list of the most essential elements of SEO, and organized them into an SEO audit template that you can use to understand how your site is performing on search engines. If you find yourself overwhelmed by this SEO audit template, then reach out to us and see if a professional SEO audit is right for you.
On-Page SEO Audit
Keyword Research
Keyword research is at the heart of any SEO effort – in this scenario, it’s the foundation of the foundational audit. With that in mind, what do we mean by keyword research?
Before we delve into what keyword research is, it’s best to understand why keyword research is so important for SEO efforts.
Search engines like Google use keywords to understand what a website is about, and through that, try to understand which websites do the best job of providing the things that someone is looking for. For example, if you are a pizza shop that constantly talks about Hawaiian pizza on your website, and someone searches for “Hawaiian pizza”, your website is much more likely to come up in search results.
Keyword research consists of identifying the keywords that best describe your business, and using them throughout your website to help search engines understand that you website relates to those keywords.
 Identifying the best keywords largely comes from analysis of monthly search volume (how many people search for a given phrase each month) and competition (how difficult it would be to rank in the top 10 results on Google for a specific phrase). We start by coming up with a massive list of terms that describe your business, and then use tools like SEMRush to identify keywords that have a high search volume and low amount of competition. For those operating on a smaller budget, try using Google's Keyword Planner to identify the best possible keywords.
Identifying the best keywords largely comes from analysis of monthly search volume (how many people search for a given phrase each month) and competition (how difficult it would be to rank in the top 10 results on Google for a specific phrase). We start by coming up with a massive list of terms that describe your business, and then use tools like SEMRush to identify keywords that have a high search volume and low amount of competition. For those operating on a smaller budget, try using Google's Keyword Planner to identify the best possible keywords.
1. Start by plugging a phrase that broadly describes a page of your site into the tool.
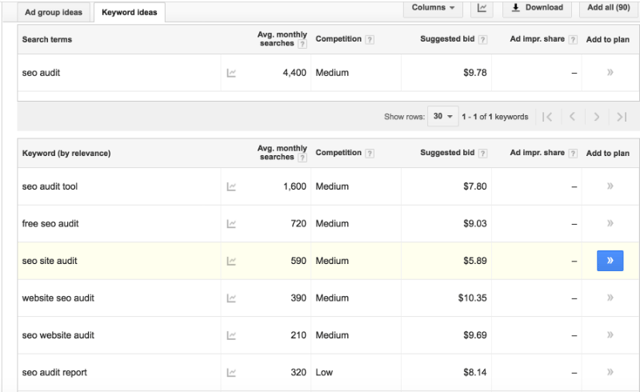
2. Export the list of keywords, and find a phrase with a low to medium competition score that accurately describes your business. This is now the focus keyword of that specific page.
3. Repeat the process for every other page of your site.
Content Quality
My favorite way to describe SEO is “writing really good content, and then jumping through a bunch of little hoops.” The reason for this is that, at the end of the day, content quality is (arguably) the single biggest factor that will determine your search rankings, largely because content quality will influence so many additional ranking factors.

Image courtesy of Rankedia.com
The man pictured above is Matt Cutts, the former head of the web spam team at Google. In other words, when you get caught trying to manipulate your website’s search rankings, he’s the guy who penalizes your website. The biggest takeaway from this is contrary to what many people think, writing good content goes hand in hand with SEO. In other words, a big part of your SEO audit should consist of reviewing the content on your website and updating outdated information, enhancing the quality of your blog articles, etc.
When evaluating your content quality, some of the first things to ask are:
- Is it actionable?
- Is it long enough - aim for 1,000 words or more?
- Is is easily digestible - is it formatted in a way that readers can easily scan through?
If the answer to any of these questions is "no", go back and revise the article.
Site Structure
Imagine trying to read a book with the pages out of order. Chances are, it would be really difficult to follow. Search engines read your website in a similar way that we read books, and have an equally difficult time understanding the content if things aren’t in the right order. Search engines have the easiest time understanding your website when your home page focuses on the big picture, and deeper pages, or URLs, go more in depth on the big picture’s encompassing topics.
With that in mind, here are a few quick tips for building a proper URL structure
- Use “-“ instead of “_”, and KISS (keep it simple, stupid – don’t use symbols or numbers when you can avoid it, and don’t need to use stop words like “and”, “a”, “or”, etc.)
- If you’ve already launched your website, it may not make sense for you to restructure all of your URLs – we normally determine this on a case-by-case basis, so feel free to reach out to us and we'll share some thoughts on whether a URL restructuring makes sense for you.
Header Tags
Imagine picking up a book that didn’t have individual chapters to it. You could read the book, but you may occasionally find yourself lost, wondering where one idea ends and another begins. Header tags are the tools on your website that help your reader (and search engines) to understand how different concepts on a page flow together. The title of the central topic of a page should be contained in an h1 tag, while the title of subtopics of this topic will be wrapped in h2 or h3 tags. For an example, look at the formatting of this post – “SEO Audit Template…”, the central topic of the page, is an h1 tag, while “on-page SEO audit” – one of the elements of a foundational SEO audit, is an h2 tag. Header tags are one of the most valuable on-site ranking factors, and are one of the best places on your site to incorporate your focus keyword, so do your best to use a close variant of each page's focus keyword within the header tags.
Title Tags & Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions are the descriptions that appear in search engines when you search for something, and offer a brief description of each result that shows up. Title tags play a large role in your search rankings, and are a great place to incorporate your page's focus keyword.
Meta descriptions aren’t a direct ranking factor any more, but creating custom meta descriptions can drastically increase click through rate, which will improve that page’s rankings
 AdVision SERP from Google
AdVision SERP from Google
Alt Text
Imagine a blind person going to visit a museum, without a guide who was able to explain everything that is sitting on display. You can be sure that they would never come back to that museum. Alt text serves a similar purpose, and is a simple description of an image that appears on visually impaired browsers in order to provide a more positive experience for website visitors.
While a small part of SEO, alt text does play a role in search engines, and as a result, should be added to every picture of your website.
Inlinks
Has a friend ever invited you to a party where you didn’t know anyone, and then failed to introduce you to their friends? If so, I’m sorry. I’ve been there too, except in my case, everyone at the party was speaking Swedish – I’m sure you can imagine what that night looked like. When you fail to link to other parts of your website, you put those pages in the same corner that I was stuck awkwardly standing in. Inlinks, or links from one page of your website to another, are your tool for introducing people to these pages, and carry a lot of weight in SEO. With that in mind, don’t forget to spread the love and set up a system of inlinks that connect the pages of your site.
It's also important to note that the anchor text, or text that the link is included in, impacts the rankings of the page that you link to. Using anchor text that relates to the topic of the page you link to will help improved the linked page's ranking for relevant keywords. The best starting point is to use a website crawling tool like Screaming Frog to identify how many inlinks each page of your site has. Highlight pages that are much lower than the average page of your site, and focus on linking to those pages more often in new pages or blog articles that you create.
Technical SEO
Sitemaps
Remember the last time you were driving around a new area and didn't have a map or GPS? You could probably navigate though the town, but finding a specific landmark would be very difficult without asking for direction. Search engines are no different, and a sitemap is the map that they need to navigate through your website. In other words, sitemaps give search engines an easy-to-read tool that makes it easy for them to reach and examine each page of your site.
Without a sitemap, search engines can still understand your site, but may miss some important sections of your site. If you’re generally driving around this new town without a map, you will probably come across some of the important parts of the town, but you might miss out on a hole-in-the wall pizza shop that everyone raves about.
The best way to check for the status of your sitemap is to visit yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml (this may bring you to a different page, but you’ll usually end up at your sitemap if you type this in). If this page doesn’t come up, then you probably need to build and add your sitemap to your site, and then submit it to Search Console to ensure that Google has access to this.
404's & 301's
Imagine that you’re using your GPS to take you to a new restaurant. If you’ve never been there before, you may take a wrong turn and find yourself slightly off course. Imagine if your GPS just said, “sorry, you’re lost,” and then shut itself off. Unless you had the patience of a saint, you would probably break that GPS. Fortunately, your GPS will fix your route and give you a slightly different way to get to your destination. 404 errors and 301 redirects work much the same way – a 404 error is simply a message that appears if you click on a link to a page that doesn’t exist (i.e. the browser tells you that you’re lost). 301 redirects are slightly altered path that gets you to the same (or a very similar) destination.
301 redirects don’t just occur naturally. Instead, you must set up 301 redirect on your own to tell the browser where to send people to if they reach a specific error page. While there are many ways to set up 301 redirects, we strongly recommend setting them up in your .htaccess file, which can be found by logging into your web hosting provider.
Duplicate Content
If your favorite author published a book, and then published the exact same book under a completely different name you’d probably be pretty confused. However, the author could easily clarify the situation by making a note at the beginning of the second book saying that book 1 was the original source. Search engines feel the same way when you publish content in two different places. While search engines may penalize you, it is much more likely that they will struggle to understand which is the original source, and will pick one of the two to index, while ignoring the other. In order to ensure that the right form is indexed, you need to set up canonical tags, which serve as the note at the beginning of the page to tell search engines where to find the original source.
Robots.txt
If you’re driving along and come across a “Road Closed” sign, you turn around and take a different road. Robots.txt serve as a “Road Closed” sign for search engines, and basically tell them not to waste their time examining certain pages. Search engines have a short attention span when it comes to crawling your website, and the last thing that you want to do is have them waste their limited attention span on your privacy policy page. Instead, you want to ensure that search engines are only examining the pages that matter. Check your current robots.txt by typing “yourdomain.com/robots.txt” into your browser and seeing what comes up. If all that you see is “Disallow: /wp-admin/”, then you probably need to block out some more pages on your site. Similarly, if you see "Disallow: /", note that search engines are being told to ignore your entire site. While this is commonly found on site that are under construction, a fully-functioning website should never contain that line of code.
Site Speed
Is there anything worse than being stuck in traffic? You know where you need to be, but you just have to sit and wait to get there. This is the reaction that every single person has when they visit your website if it takes more than a few seconds for the page to load. In fact, about 15% of all people will leave your website immediately if it takes more than 2 seconds to load. Go into Google Analytics and check your average page load time. If the load time is more than 1 second, you have some work to do. Start by exploring these tips on how to increase site speed.
Mobile Friendly
It's no secret that mobile Internet usage has drastically increased over the past few years. Last April, Google released an update to their search engine which started to heavily penalize website that aren’t “mobile friendly” (i.e. websites that are a pain in the ass to view on your phone). You can always check how mobile friendly your website is here, but the simplest way to check whether or not your website is mobile friendly is to try visiting it on your phone. If the experience is no good, then it’s probably not mobile friendly.
Off-Page SEO Audit
Link Building
Earlier in this post, I mentioned that content quality is arguably the most important ranking factor. Those who disagree with that statement would instead say that link building is the single most important ranking factor. Regardless of which directly counts for more, the point is that this is really important.
Link building is the process of getting other websites to link back to your website, and the more reputable these websites are, the more “points” you get for the link. With link building, it’s important to note that links from “spammy” websites can actually hurt your search ranking, so as a general rule, never pay for links, or request links from low quality websites (download the Moz bar and avoid websites with a spam score above 4 or 5 like the plague).
 Spam Score from Moz.com Results
Spam Score from Moz.com Results
Before delving into link building, it’s important to take time to evaluate your existing links. At AdVision, we use Ahrefs to do this, but there are countless tools that enable you to evaluate your current link status. Start out by examining how many links you have lost over the past year, and then evaluate your existing links to disavow spammy links.
Social Media
With the rise in social media usage over time, search engines have started to take social media into account more and more when evaluating a website. Search engines examine how many followers your company account has, and how many times your blog articles are shared on various social media channels. When analyzing your social media channels, examine how many times your blog articles have been shared, and how active you are on your various social media profiles.
Local SEO
As I wrote in my last local SEO article, local SEO is the best way for small businesses to compete with national companies. Picture that you’re sitting at home one night, and decide that you really want a pizza. If you ask your roommate for a pizza suggestion, he’s not going to tell you about a Papa John’s pizza shop an hour away from your apartment. Instead, he’ll try to recommend a pizza shop that you could walk or drive to. Search engines focus on doing the same, and will provide a ranking bonus to businesses that are located close to someone who is searching for what they offer. So your pizza shop probably won’t ever outrank Papa John’s on a national search level, but you can win on a local level.
Want to evaluate your local SEO? The best place to start is to ensure that your business is listed in all of the major directories like Yelp and Google My Business. Come explore our local listings scanner to see how your site is performing.
Final Thoughts
Keep in mind that SEO is not a short-term effort. While implementing these audit suggestions can drastically improve your organic search rankings,this is just the first step towards showing up on the first page of Google. First page search results requires continuously creating great content and promoting that content. Come explore our inbound marketing services to see how we accomplish this.
Have any questions about running your own SEO audit? Contact us and we’ll be happy to help!

February 9, 2016